With PowerPivot (codename: Gemini) for Excel 2010 users can work with loads of company data as never before. With PowerPivot, as an end user, you can create your “own cube” within Excel and simply slice and dice through these tons of information.
In this exercise, you will learn how to import and prepare data from a SQL Server 2008 R2 database into the Microsoft Project “PowerPivot” Add-in for Microsoft Office Excel 2010 (PowerPivot).
Requisites:
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
PowerPivot module installed
Excel 2010
ContosoRetailDW (2008 R2 database, you can download this one from codeplex or Microsoft site.)
Exercise 1: Getting started
By the end of this exercise, you will understand:
· How to launch PowerPivot
· How to connect a PowerPivot to an external data source to the PowerPivot
· How to control what data is imported into PowerPivot
· How to create a calculated column using a Data Analysis Expression formula
|
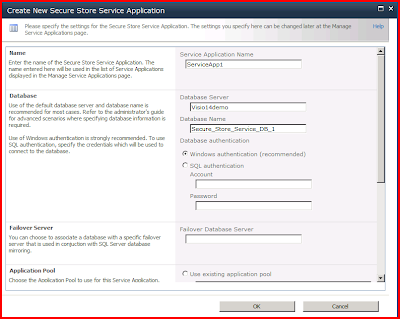
· Click Start, All Programs, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Excel 2010 (Beta) · Click the PowerPivot tab. · Click the PowerPivot window button to start the PowerPivot add-in. The add-in loads a new top-level window entitled PowerPivot Client Window.
|
· In the PowerPivot Client Window, click the From Database button, and select From SQL Server from the list of data sources. · In the Server name field, enter localhost. · In the Database name combo-box, select ContosoRetailDW from the list. The wizard automatically creates a Friendly connection name. · Click the Next button to continue the running the wizard. · On the Choose How to Import the Data page, choose the Select from a list of tables and views to choose the data to import option and click Next.
· From the list of available tables, scroll down and place a check next to the FactSales table. · Click the Select Related Tables button to have the wizard select those tables related to FactSales. The wizard displays a message that “6 related tables were selected”. · With the FactSales table still selected, click the Preview and Filter button. The wizard opens a new window where you can filter the data that it imports.
· Remove the check for the SalesKey column.
|
· Scroll to the right until you can see the CurrencyKey column. Remove the check from the CurrencyKey column.
· Click OK to apply the filter and return to the wizard. Notice that the Filter Details column now shows Applied filters.
· Click on the table name FactSales in the Friendly Name column and change the name to Sales.
· Click Finish to start the import and prepare process.
Note: As the import process progresses, the dialog provides you with information about the number of rows transferred.
Note: Notice how PowerPivot has transferred almost four million rows from the Sales table. With more memory, you could work with 100 million row datasets.
· Once the import process is complete, click the Details button in the Message column to review any status messages. Generally you only need to do this if any errors occurred.
· Click OK, then Click Close to close the wizard and return the PowerPivot Client Window.
· At the bottom of the window, you will see a tab for each imported table. Right click on the DimChannel tab and choose Rename from the context menu.
· Change the name to Channel. You can rename the tables to make it easier for you to work with them.
· Click on the Sales tab.
· Scroll all the way to the right until you can see the Add Column column.
· Select Add Column.
· In the formula bar enter =[SalesAmount] – [TotalCost] and press Enter. PowerPivot creates the new column and updates the screen with your calculation.
· With the new CalculatedColumn1 column selected, right click and select Rename Column from the context menu.
· Type Profit to change the column name and press Enter.
· Click the PowerPivot button in the upper left corner of the application window and select Save.
· Change the path to the desktop and name the file ContosoSales.xlsx and click Save.
· Once PowerPivot has saved the file, continue to the next exercise.
Exercise 2: Work with data
In this exercise, you create a sales report in Excel 2010 using PowerPivot as your in-memory data source containing almost four million rows.
By the end of this exercise, you will understand:
· How to create a PivotTable and PivotChart report connected to PowerPivot
· Use data slicers to filter data
Note: Exercise 2 assumes you have completed Exercise 1 and that Excel 2010 and the PowerPivot Client Window are still open.
· If necessary, click the ContosoSales.xlsx button on the Task Bar to activate the PowerPivot Client Window.
· Select the PivotTable button and from the drop-down menu, choose the Chart and Table (Vertical) menu option. PowerPivot will return you to Excel window.
· In the Insert PivotTable dialog, choose the Existing Worksheet option and click OK.
· In the PowerPivot Task Pane, scroll to the bottom of the list of tables until you find the Sales table. Then find the Profit field and place a check next to it.
· Next, find the ClassName field in the DimProduct table. Drag and drop it into the Axis Fields box.
· Now find the ChannelName field in the Channel table. Drag and drop it into the Row Labels box.
· Place a check next to the TotalCost field in the Sales table. You should note that Excel adds it under the existing Profit field in the Values box and to the right of the Sum of Profit column in the PivotTable.
· Click the drop-down menu on the Sum of Profit field in the Values box and select Move Down.
· Click on the chart, and then place a check next to the SalesAmount field in the Sales table.
· Click the drop-down menu on the Sum of SalesAmount field in the Values box and select Move to Beginning.
· On the PivotTable, select the cell with the text Row Labels (it should be cell A1). Change the value to Class / Channel.
· Change the Sum of SalesAmount column header to Sales Amount.
· Change the Sum of TotalCost column header to Total Cost.
· Change the Sum of Profit column header to Profit. The headers should now all be changed.
· Highlight all of the cells in the PivotTable that contain numeric figures.
· Click the Home tab on the Ribbon followed by the $ symbol to format the selected values.
· Next, click the Format button and from the drop-down menu, choose the AutoFit Column Width command.
· Select the Sheet1.
· On the PivotChart, select the Y Axis label, then right click and select Format Axis.
· In the Format Axis dialog, change the Display units to Thousands.
· Choose the Number option from the list of pages.
· Choose Currency from the Category list.
· Change the Decimal places to 0 and click Close.
· Choose the Number option from the list of pages.
· Choose Currency from the Category list.
· Change the Decimal places to 0 and click Close.
· If you would like to resize the chart. Click the right side of the charge on the grab handle. Drag to left until it is the width that you desire.
· In the Gemini Task Pane, locate the GeographyKey field under the DimStore table. Drag and drop it to the Slicers Horizontal box.
· Find the PromotionName field in the DimPromotion table. Drag and drop it to the Slicers Vertical box.
· Finally, locate the Manufacturer field in the DimProduct table. Drag and drop it to the Slicers Vertical box.
· Right click on the Horizontal Slicer: GeographyKey, and select Slicer Settings.
· Change the Caption from GeographyKey to Country and click OK.
· Repeat the process and change the title of the first Vertical Slicer from PromotionName to Promotion.
· In the Country slicer, select only one of the fields such as 731. Notice how the PivotChart and PivotTable update in real time. Play around with other slicers to get a feel for how the real time analysis works.
· Close Excel by clicking the File and select Exit.
· If prompted to save your changes, do so. Excel will close the PowerPivot Client Window.